Strength and Concentration of Acids and Bases
Strength and Concentration of Acids and Bases: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Concentrated Solution, Dilute Solutions, Strength of Acid and Base Solutions and, Reactions of Metal Carbonates with Acids
Important Questions on Strength and Concentration of Acids and Bases
Define dilute solutions with an example.
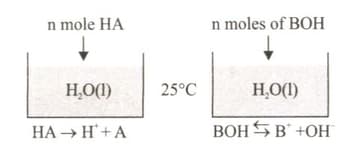
In Figure - 1 and Figure - 2, equal moles of and substances are added to the same volume of pure water at the same temperature. The equations for the solubility of these substances in water are given thereafter.
(i) The number of moles of vessel 1 equals the number of moles of in vessel 2.
(ii) The electrical conductivity of (in water) is higher than that of (in water).
(iii) The number of moles of ions in (water) is greater than the number of moles of ions in (water).
Which of the statements out of are correct?
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
Mineral acids are completely ionized in an aqueous solution.
Mineral acids are partially ionized in an aqueous solution.
Carboxylic acids are completely ionized in an aqueous solution.
Carboxylic acids are partially ionized in an aqueous solution.
Codes:
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acidic strength?
A sample of soil is mixed with water and allowed to settle.The clear supernatant solution turns the pH paper yellowish-orange.Which of the following would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish-blue?
Which of the following has calcium carbonate as its component?
The aqueous solution of which of the following substance is a good conductor of electricity?
Iman and Arianna were given four different powders. They had to design a way of finding out if the powders were metals, carbonates or neither.
Here is their plan:
A: Add one spatula of powder to a test tube.
B: Add of hydrochloric acid to the test tube.
C: Fit a bung loosely on top of the test tube.
D: If the powder bubbles, remove the bung and hold a lighted splint close to the top of the tube.
E: Repeat steps A and B. Fit a bung with a delivery tube into the test tube — put the other end of the delivery tube into a test tube of limewater.
Here are their results:
| Powder | Observations when the acid is added | Observations when a light splint was used | Observations when the gas was bubbled through limewater |
| 1 | Lots of bubbles produced quickly | Heard a pop noise | No change |
| 2 | No bubbles | No change | No change |
| 3 | A few bubbles produced slowly | Heard a pop noise | No change |
| 4 | Lots of bubbles produced quickly | Flame went out | Limewater went cloudy |
What can be said about powder 4?
A solution that has a relatively small amount of dissolved solute is called as:
Which of the following is not an example of dilute solution?
The chemical used in fire extinguishers is
The acidic and basic strength of solution is based on _______________ ion concentration.
A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime water milky. The solution contains:
Cotyledons are also called-
Depending upon the amount of solute present in a solution, it can be called a ________ solution.
How do metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids?
Metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids to give